Designing, creating and refining algorithms
Creating, Interpreting, and Refining Algorithms
Understanding how to create, interpret, and refine algorithms is crucial for problem-solving in computer science. Here’s a guide on using pseudocode, flowcharts, and high-level programming languages to achieve this.
Pseudocode
Pseudocode is a plain language description of the steps in an algorithm. It combines the structure of programming languages with the readability of natural language.
Example
BEGIN
INPUT age
IF age >= 18 THEN
PRINT "You are an adult."
ELSE
PRINT "You are a minor."
ENDIF
END
Flowcharts
Flowcharts visually represent the flow of an algorithm using symbols to denote different types of actions or steps.
Common Flowchart Symbols
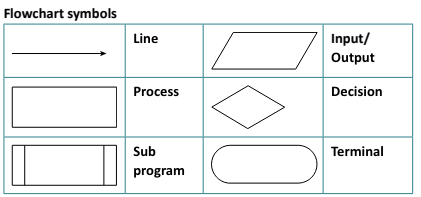
- Line: Indicates the flow of the process.
- Input/Output: Parallelogram shape, used for input and output operations.
- Process: Rectangle shape, represents a process or operation.
- Decision: Diamond shape, represents a decision point.
- Subprogram: Rectangle with double-struck vertical edges, used for invoking a subroutine or subprogram.
- Terminal: Oval shape, represents the start or end of the process.
Example
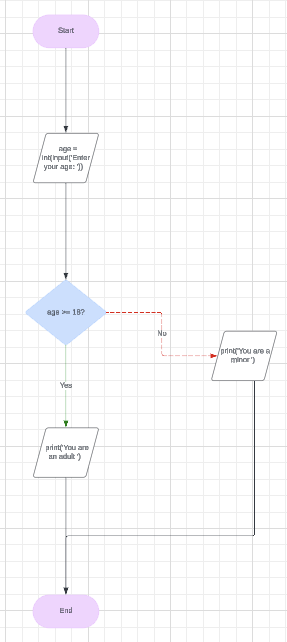
High-Level Programming Language
High-level programming languages, like python, Java, or C++, are used to implement algorithms in a form that can be executed by a computer.
Example in python
age = int(input("Enter your age: "))
if age >= 18:
print("You are an adult.")
else:
print("You are a minor.")
Complete, Write, or Refine an Algorithm
To complete, write, or refine an algorithm using these techniques, follow these steps:
- Define the Problem: Clearly understand the problem you need to solve.
- Draft with Pseudocode: Outline the logic using pseudocode.
- Visualize with Flowcharts: Create a flowchart to visualize the algorithm’s flow.
- Implement in Code: Write the actual code in a high-level programming language.
- Test and Refine: Run tests to ensure the algorithm works correctly and refine as needed.
Example Task
Task: Determine if a number is even or odd.
Pseudocode
BEGIN
INPUT number
IF number MOD 2 == 0 THEN
PRINT "The number is even."
ELSE
PRINT "The number is odd."
ENDIF
END
Flowchart
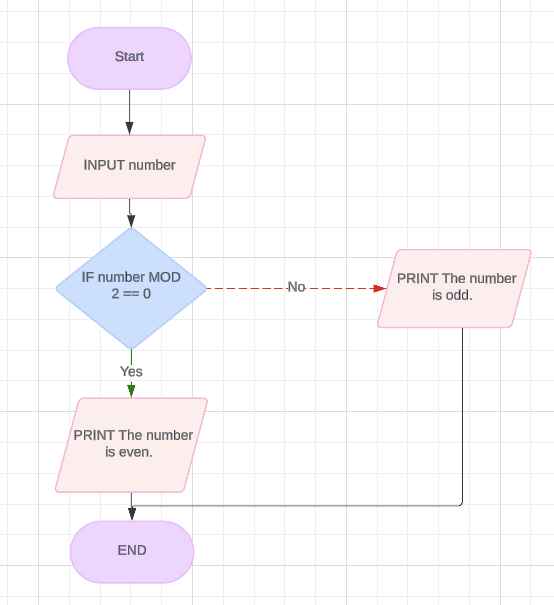
number = int(input("Enter a number: "))
if number % 2 == 0:
print("The number is even.")
else:
print("The number is odd.")